December 12, 2012
How does caffeine affect the human body? How much coffee or tea a day will not cause harm? Is it possible to get poisoned by caffeine? Let's figure it out.
Caffeine is rightfully considered one of the best natural stimulants. It reduces the feeling of fatigue, increases attention and improves mood. The main sources of this substance are coffee, tea, mate and chocolate. How does caffeine affect the human body? How much coffee or tea a day will not cause harm? Is it possible to get poisoned by caffeine? Let's figure it out.
What is caffeine?
Caffeine is a substance that is found naturally in the leaves and seeds of many plants.
Man also learned to create an artificial analogue, the formula of which is C8H10N4O2, and use it in food. Caffeine has medicinal properties and is used as a stimulant of the central nervous system, causing increased activity. Most people respond to this substance with increased energy and improved mood.
Caffeine is found in tea, coffee, chocolate, various soft drinks, and is also part of painkillers. Natural caffeine has a bitter taste, but in many products this bitterness is masked by processing.
Content:
- What is caffeine?
- Metabolism
- Effect on the body
- Caffeine overdose
- How does it get into the blood?
- Caffeine and pregnancy
- Effect on the stomach
- Side effects
- Harmful properties
- Effects of quitting caffeine
- How to safely quit caffeine
- Benefit for health
- Invigorating springs
The main sources of this substance for teenagers are energy drinks and other soft drinks. Their “work” is noticeable, as a rule, for 6 hours. True, sensitivity to caffeine is an individual indicator. Typically, the younger the person, the less of the substance is needed to feel its effects. Individuals who regularly consume caffeinated beverages become less sensitive to this energizing component over time. This means that they will need to increase the dose again and again to achieve the effect.
Why does a person fall asleep?
Humanity has been dealing with sleep issues for a very long time, but this topic (like any other) has not been fully studied, although there are a number of good concepts. Pioneers in sleep research hypothesized that there was a sleep factor, a substance that accumulated during the day and caused drowsiness [1]. It is believed that the Japanese physiologist Kuniomi Ishimori was the first to try to isolate the sleep factor [2]. Also among the first were René Legendre and Henri Piéron, who induced sleep in dogs by injecting them with a substance obtained from the brains of other sleep-deprived dogs [3].
Modern scientific evidence suggests that adenosine is well suited for the role of a sleep factor. Adenosine, a ribonucleoside consisting of adenine and ribose [4], plays a huge role in our body. It is a component of the genetic material of cells, in addition, it is part of the “energy” compounds in our body - such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It has a number of other functions, but for the purposes of this article, the interesting one is its role as a signaling molecule with broad physiological effects, both in the brain and beyond. For its functions, adenosine was even nicknamed the signal of life [5] and the body's natural defense [6].
Metabolism
Once in the body, caffeine is metabolized into dimethylxanthine derivatives (paraxanthine, theobromine, theophylline), then into monoxanthine, and then into the xanthine molecule. Other metabolic products are di- and trimethyl allantoin, uric acid and uracil derivatives.
Caffeine is easily distributed in plasma, intercellular fluid and inside cells. It also circulates in extracellular adipose tissue. By the way, people who smoke metabolize caffeine faster. Also, differences in the speed of the process may occur among people of different nationalities, which is explained by a genetic factor. But there is practically no difference in the rate of absorption between women and men.
Our body is able to absorb these “energizing molecules” quite quickly. But it also quickly gets rid of them. Caffeine is metabolized primarily by the liver and has a relatively short half-life. Usually 5-7 hours are enough to get rid of half of the resulting substance. For this reason, the cup of coffee you enjoyed before lunch will definitely not prevent you from falling asleep in the evening.
Caffeine can be synthetic or natural (obtained from plants). It is possible to determine the difference between them only in the laboratory. The concentration of any of these substances in the body can be measured by examining saliva, since this substance accumulates primarily in liquids in the body. Caffeine can enter the body through the mucous membranes of the cheeks. Chewing gum containing the substance is characterized by faster absorption compared to drinking coffee, since in the form of a drink, caffeine must first pass through the stomach and intestines, and only then enters the blood.
A little history and chemistry
Caffeine
It was first discovered in 1819 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge. While studying coffee and the elements it contained, Runge isolated a new substance, previously unknown to people, to which he gave the name “caffeine” (caféine from the French word café - coffee). Later it turned out that this molecule is present in many plants, being primarily a natural insecticide and only secondarily a natural stimulant of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Thein
8 years later, in 1827, the Dutch organic chemist Gerrit Jan Mulder conducted a similar experiment (but not with coffee, but with tea) and discovered... yes, a substance suspiciously similar to caffeine. But, since it was found in tea, it was given the name "theine" - from the English word "tea" (tea).
The same molecule?
What happened next? And then Mr. Mulder thought for a long time and already in 1838 (that is, 11 years after his discovery) shocked the scientific community with the news that caffeine and theine are actually the same thing. In both tea and coffee, the substance has exactly the same structure and is a molecule of the formula C8H10N4O2. The same molecule is also found in mate tea (matein), guarana leaves (guaranine), cocoa and kola nuts.
Effect on the body
Caffeine is a product of plant origin, the highest concentration of which is found in coffee beans, tea leaves, soft drinks, chocolate, and cocoa beans.
Also found in some medications (painkillers, allergies, colds and weight loss). In fact, from a chemical point of view, caffeine is a pain reliever and also a substance that enhances the effects of other pain-relieving drugs.
Modern data on caffeine is very contradictory regarding its beneficial and negative effects on the human body.
It is believed that for healthy people, 300 mg of an invigorating substance per day is a normal portion that is not harmful to health. Meanwhile, in some cases it is important to limit the consumption of the substance. Large portions (more than 700 mg per day) help remove calcium and magnesium from the body. It was previously believed that caffeine was one of the causes of osteoporosis. Meanwhile, recent studies have shown that calcium losses caused by caffeine from 1 cup of coffee can be easily compensated for by 2 tablespoons of milk. But in people who are especially sensitive to even minor calcium losses, caffeine can actually cause bone problems. For this reason, women after menopause should not abuse caffeine-containing products, since they are already at risk of developing osteoporosis.
It also acts on the body as a mild diuretic. But again, don't worry that foods containing this substance can cause dehydration.
When talking about caffeine, many people think of coffee first. But this is far from the only source of the substance. Tea, cola and other drinks also contain caffeine. And this explains why, according to research, children aged 6-9 years consume approximately 25 mg of the energizing substance daily, and their parents may not even realize it. Meanwhile, children sensitive to it develop irritability and anxiety.
Caffeine acts as a stimulant, affecting the central nervous system. In the body, this substance begins to act approximately 15 minutes after administration and this effect lasts up to 6 hours.
What is caffeine?
Caffeine is a natural nervous system stimulant found in coffee, tea and cocoa beans. Currently, there is an increase in cases of caffeine overdose with many ensuing problems. Moreover, thanks to recent scientific advances, we now know that there is a gene responsible for the metabolism of caffeine. For many it is changed or absent, and therefore some should be more careful. In order for each of you to control your own caffeine consumption, we decided to tell you how much caffeine is contained in various caffeine-containing drinks and how to influence it.
Why do plants need caffeine?
To begin with, I would like to generally understand why the plant produces caffeine? Unlikely for you and me. In fact, from an evolutionary point of view, we are all selfish and any of our actions is aimed at protecting ourselves from environmental aggression factors. The coffee tree also began to produce caffeine so that it would not be harmed by various insects. There are fewer insects at higher elevations, which means there is less caffeine in such plants, and more flavonoids, terpenes and polyphenols, which are antioxidants - they account for most of the benefits of coffee.
Chemical structure of caffeine
The chemical structure of caffeine is an alkaloid. Caffeine has no odor, but only a bitter taste. The aroma of coffee comes from flavonoids, polyphenols and terpenes. Based on this, the hypothesis about the relationship between tree growth height and caffeine content is confirmed. Coffee from Ethiopia, which grows quite high, will have more acidity and less caffeine. Unlike Brazil, which will have more bitter notes and more caffeine. To keep it simple, you can use the following principle: the more bitter you taste in your cup, the more caffeine it contains. For example, enthusiasts conducted a study and measured the amount of caffeine in coffee from different countries:
Based on the results of the study, we can conclude that Starbucks sells some of the most caffeinated drinks in the world (we'll talk more about this at the end, so keep reading).
What determines the caffeine content?
1. Coffee type
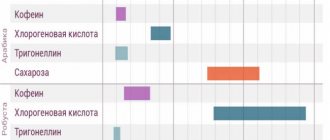
The two most famous varieties of the coffee tree are Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora, better known as Arabica and Robusta. They differ greatly in taste and chemical composition. Arabica contains average amounts of caffeine, amino acids and chlorogenic acid (the main coffee antioxidant), and also has 60% more oils than robusta, which is high in caffeine and high in chlorogenic acid.
2. Roasting
There are many questions and controversial issues here. Many people believe that the coffee bean itself, regardless of the intensity of roasting, always has the same amount of caffeine, but this is not true. According to the study, green beans have 30% more caffeine than dark roasted beans (the study was conducted on Brazilian beans). Based on this, we can conclude that caffeine is destroyed when heated. For example, we can compare the compositions of starbucks light roast coffee (360 mg of caffeine in 473 ml) and dark roast (260 mg in 473 ml).
3. Number of grains
It is necessary to take into account that during roasting the coffee bean inflates (due to the release of CO2) and loses moisture, accordingly its weight decreases, and the concentration of various substances and volume increase. To make it clearer, imagine 2 glasses. Place 50g of dark grain in glass A, and 50g of light grain in glass B. So there will be more grains in quantity in glass A (with dark grains), despite the fact that the weight is the same. Thus, it may turn out that in the end there will be more caffeine in coffee made from dark roast beans, since more beans were used in quantity.
4. Temperature
Cold water is worse at extracting organic acids and other substances, including caffeine. Therefore, cold brew contains approximately 30% less caffeine than filter coffee.
5. Grinding
The finer the grind, the greater the contact area between the coffee particle and water, and, accordingly, the extraction of all substances, including caffeine, is greater.
An American study measured how three grind types (fine, medium and coarse) and different brewing methods affected the chemical composition of coffee. As a result, it was revealed that filter coffee became the leader in one serving of the drink in terms of antioxidant activity and polyphenol content in coffee, followed by espresso and cezve/Turkish coffee. The caffeine content was 316.112 and 64 mg in filter coffee, cezve/turk coffee and espresso coffee, respectively.
6. Amount of water
Water is a universal solvent. The more water, the more caffeine we will extract from the grain. This information was also proven by an Italian study, which also found that espresso has the lowest pH (meaning higher acidity) - 5.41, then cezve/turk coffee - 5.70, and finally filter coffee - 6.09. However, it is worth considering that in this study, filter coffee was made with dark roasted beans, but usually they still use light or medium roasted beans, which means they will have higher acidity.
Knowing points 4 and 5, we can now talk about a study in which we took three 25 ml cups of espresso and measured the caffeine content. We used grind sizes 6, 6.5 and 7.0. The caffeine content was found to be 77.44, 105.83, and 98.97 mg, respectively. Based on this, we can conclude that with the finest grinding, the amount of water passing through the tablet decreases, and accordingly, the amount of caffeine decreases, even despite the maximum contact area. That is, for more caffeine in espresso, you should maintain a balance and choose a medium grind. And, if the goal is to achieve the maximum concentration of caffeine in a coffee drink, and not in espresso, then you should grind the coffee as much as possible and then pour in a sufficiently large amount of hot water.
A Practical Study of Caffeine in Beverages
In this study, the researchers prepared 25 ml espresso multiple times without changing the grind size using a Super Jolly Coffee Grinder for Grocery, Mazzer, Italy. The extraction time varied from 13.5 to 17 seconds due to the fact that the variability of the particles in the grind was different each time, and accordingly the amount of water passing through varied. Ultimately, caffeine results ranged from 80 to 130 mg. From this we can understand that each time, due to the difference in preparation, the amount of caffeine will be different.
However, there is one more important thing - the grain also contains a different amount of caffeine each time. Some curious people decided to conduct a study in which they bought the same pack of coffee from the well-known company Starbucks every day for 6 days in the same store.
Based on the fact that the results vary by almost 2 times, we can conclude that even such a large company as Starbucks cannot supply coffee with a always standard amount of caffeine. This is a very variable process, depending on many factors, and is not yet controlled by anyone.
Recommended caffeine intake in mg - how much will it be in cups?
I would also like to remind you that food and drinks are a huge factor influencing a person and coffee is no exception. Thanks to caffeine, it has a very strong stimulating effect, so it is advisable not to consume it 5-7 hours before bedtime, as disturbances may occur with sleep, which is the most important period of recovery for the body. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) believes that consuming caffeine up to 400 mg per day does not pose any danger to an adult (excluding pregnant women and the elderly), therefore, recalculating this dose into more understandable cups, we find that you can drink one cup per day filter coffee (~316 mg of caffeine), three cups of cezve/turk coffee (~336 mg of caffeine) and as many as five cups of espresso (~320 mg of caffeine).
As a bonus, we decided to tell you an interesting fact. Starbucks sells coffee with more caffeine than its competitors. It is not clear how and why they do this, but it is a fact. Even their decaf line contains 25 mg of caffeine, and the usual one reaches up to 360 mg, despite the fact that on average everyone has about 300 mg maximum.
Coffee with the highest caffeine content in the world
While researching the topic of this article, we discovered that there are brands in the world that sell coffee with extreme caffeine content, which can reach up to 1555 mg per 354 ml, which, according to the most loyal recommendations, is at least 4 times the daily requirement. And what’s most interesting is that many of these beans are Arabica, and not Robusta, as many might think.
At the end of this article, I would like to say that coffee is a rather complex drink, which, in addition to caffeine, contains a whole storehouse of other useful and potentially dangerous substances. The scientific and medical communities have not yet formulated any clear position regarding the use of coffee, but everyone is absolutely sure that filtered coffee is the safest, since the filter itself traps many harmful substances. At the same time, when passing coffee through a filter, it is still worth remembering that moderation is important in everything and you should not consume more than 400 mg of caffeine per day.
And we will talk about exactly what harmful substances the filter retains and, in principle, what else is contained in coffee, besides caffeine, in the following posts.
Elements of the works of illustrator Peter Slattery were used in the design of the article.
Caffeine overdose
Consuming moderate doses (up to 250 mg of brewed coffee or 500 mg of cola) helps people concentrate and relieve drowsiness. But higher doses increase heart rate, raise body temperature, increase blood flow to the skin and extremities, increase blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and also stimulate the secretion of stomach acid, acting as a diuretic.
With excessive consumption of the substance, people may experience dizziness, hypoglycemia, nausea, rapid breathing and heart rate, confusion, irritability, insomnia, changes in appetite, dry mouth and other side effects. But contrary to popular belief, caffeine cannot neutralize alcohol in the body.
How to make decaffeinated coffee
A caffeine-free drink is made by decaffeination. Decaffeination of various natural products is a valuable by-product that is used in the preparation of various drugs.
Decaffeination at home is the process of treating green coffee with an aqueous solution with aromatic oils that “pull out” the caffeine. Now about 20% of drinks are sold in which the decaffeination process was carried out on an industrial scale by another method. Coffee is not a desirable drink during pregnancy.
Quantification methods
In order to maintain optimal levels of this compound in foods and drugs, various concentration determination methods have been developed. Monitoring is a very important aspect as its consumption in higher doses can lead to a variety of physiological disorders.
There are methods used in the analysis of the compound in environmental samples such as pharmaceuticals, soft drinks, energy drinks, tea and coffee.
Spectrophotometric measurements are the most popular analytical tool in the analysis of various compounds in simple and complex mixtures.
Some researchers are focused on the use of chemometric methods (at the intersection of chemistry and mathematics).
The amount of caffeine released depends on the temperature of the water used for brewing and the brewing time and is independent of the volume of water used for brewing. A good solution is the chicory coffee drink, which has its pros and cons.
How does it get into the blood?
Once in the body, caffeine is absorbed in the intestines by almost 99%. And the concentration of the substance in the body can reach up to 10 mg per 1 kg of weight. The entire absorption process occurs within approximately 45 minutes after ingestion, and caffeine reaches its peak level in the blood within 15-20 minutes. But these are rough estimates, since in each case the rate of absorption of substances depends on physiology and the source. Caffeine is absorbed slowest from chocolate and cola, while caffeine from coffee drinks and substances in tablet form is absorbed faster. But still, it is absorbed most quickly from chewing gum - through the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Chlorogenic acids
The main part of the phenolic compounds in coffee consists of chlorogenic acids. These are esters of two acids - quinic and cinnamic. Scientists also discovered esters of ferulic and caffeic acids in coffee beans. There are about a dozen different compounds in chlorogenic acids. If raw coffee contains 7-10% chlorogenic acids, then roasted coffee contains 2.5 times less. This is explained by the fact that acids are destroyed during heat treatment of grains. At the same time, the proportion of quinic acid and caffeic acid in coffee increases. Chlorogenic acids have also been found to directly affect the color of roasted coffee.
Side effects
Consuming caffeine in moderate doses generally does not have any harmful side effects on the body. Although some researchers convince that regular consumption of 100 mg of coffee daily can subsequently cause infertility, heartburn and intestinal dysfunction.
Consuming high doses of caffeine deprives you of sleep, and a person stops noticing the body's signals about the need for rest. Meanwhile, it is important to understand that caffeine does not replenish energy reserves or prevent emotional fatigue. It simply blocks the body's physiological needs for rest. Over time, this condition leads to the development of depression, causing anxiety, excessive nervousness, sweating and tremors.
Are tolerance and addiction the same thing?
It is necessary to distinguish between these two concepts. If addiction means the body's need for caffeine, then tolerance means the body's immunity to caffeine. What does it mean? This means that caffeine does not exhibit its physiological effects for a number of reasons.
How does caffeine tolerance develop? There are a number of concepts for its formation. A striking example is the concept of an increase in the number of adenosine receptors in response to long-term intake of high doses of caffeine [14], [34]. How does all this happen? See Figure 5 and read the text below.
Figure 5. Mechanism of caffeine tolerance formation. The picture shows the consistent change in the effect of caffeine on the body. At first, caffeine has an invigorating effect, but then has no effect on the body due to the formation of new adenosine receptors. An increase in the number of filled circles reflects an increase in the amount of adenosine, caffeine and improved well-being. A decrease in the number of filled circles reflects the opposite processes.
drawing by the author of the article
I'll use one of the main sources of caffeine - coffee. Caffeine tolerance is typical for people who drink coffee in large quantities and on a regular basis. This usually happens in the morning or during a break between work/study. They drink it for various reasons: it helps them wake up, it smells delicious, it gives them energy, or they want to feel like they’re part of that crowd running around the metropolis (fashionable, in short). Well, in general, after drinking coffee, a person feels like “king of the hill.” You don’t want to sleep, your heart starts beating faster, you feel an incredible surge of energy, and sometimes you want to go to the restroom. The mechanism here is still the same - blocking adenosine receptors.
The fact is that with chronic caffeine consumption, adenosine cannot attach to its receptors. The body sees that there is a lot of adenosine, which means it has nowhere to cling to - there are few receptors! In response to this, new adenosine receptors are synthesized in the brain. This is where adenosine successfully interacts with them, and the person begins to feel drowsiness and fatigue, although he continues to drink coffee in relatively large quantities.
So, one regular dose of caffeine is no longer enough. The person begins to drink more. And everything goes the same way. At first it will help, but then it won’t (new receptors are formed again). I hope you get the point.
Harmful properties
Some studies suggest that caffeine may be harmful to your health. Here are some arguments in favor of this.
- Consuming more than 4 cups of coffee per day leads to early death. Research shows that this dose, taken daily, is enough to increase the risk of sudden death by 21%.
- Increases blood pressure. In people suffering from arterial hypertension, after 2 cups of coffee, blood pressure rises over the next 2-3 hours.
- Increases the risk of cardiac diseases at a young age. Drinking 4 cups of coffee daily is enough to quadruple your risk of heart attack.
- Caffeine can trigger the development of gout.
- Provokes the formation of cysts in the mammary glands in women. It is enough to consume 30 mg of coffee per day to increase the chances of fibrocystic mastopathy by one and a half times. And women who drink 500 mg of coffee are 2-3 times more at risk of cystitis.
- Causes urinary incontinence. People who consume the drink regularly and in large doses are 70% more likely to experience incontinence than others.
- Causes insomnia.
- Causes stomach upset. Especially if you drink coffee on an empty stomach.
- Excessive caffeine consumption provokes headaches.
- Caffeine leads to impaired fertility in women: the chances of getting pregnant are reduced by 27%.
- The risk of miscarriages increases: it is enough to drink 2 servings of coffee daily for several weeks before conception.
- It worsens the health of diabetics because it disrupts glucose metabolism.
- May cause overdose or allergy symptoms.
- Accelerates heart contraction.
- Exacerbates the symptoms of menopause.
- Increases anxiety and depression.
- Caffeine lovers consume more glucose, which is fraught with obesity and diabetes.
- It suppresses collagen production in the skin.
- Makes bone tissue more fragile, which increases the risk of fractures.
What's the result?
Caffeine is the most widely used psychostimulant substance, which has both positive and negative effects on our body, therefore its consumption should be approached rationally. Therefore, the next time you have a deadline, before you drink a couple of cups of coffee or energy drinks, think, maybe it’s better to sleep? (This is if the deadline is not tomorrow morning, God himself ordered it, of course.) Well, if you drink several cups of coffee a day, then I hope this article will be the impetus for you to create a new useful habit (reduce caffeine consumption)!
To better understand and consolidate this information, I highly recommend re-reading this article again, going to the cited literature, watching videos on YouTube (for example, this one: original in English and version in Russian translation) or printing out my poster (Fig. 6).
In conclusion, I would like to thank all the people who helped me identify and correct errors in this article.
Figure 6. Effect of caffeine. You can download the poster in pdf format from this link.
drawing by the author of the article
Effects of quitting caffeine
People who stop drinking caffeinated drinks may experience discomfort and deterioration in the first 12-24 hours. Typically, the first side effects of caffeine withdrawal include headaches, irritability, nausea, nervousness, and muscle tension. But these symptoms last no longer than a week. Then the body finally adapts to a new way of life.
In order to avoid side effects, experienced people advise switching to a caffeine-free life gradually - reducing the amount of substance consumed every day.
Is caffeine addictive?
If you follow the latest ISD-11 (International classification of diseases, 11th revision - ICD-11, International Classification of Diseases 11th revision) from the World Health Organization, then yes, caffeine addiction is a mental disorder [25]. The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edition) from the American Psychiatric Association identifies caffeine use disorders as an area for further research [28], [29]. . Also, the DSM-5 describes a diagnostic scheme with nine criteria for making a diagnosis of Caffeine Use Disorder [29], [30]. Below are three main ones:
- Constant and unsuccessful attempts to reduce and control caffeine intake.
- Continued use of caffeine despite knowledge of a physical or psychological problem.
- Withdrawal syndrome or the use of caffeine to relieve this syndrome.
It is important to note that not all people become addicted to caffeine. For its development, certain conditions are necessary (high dosages of caffeine, simultaneous consumption of various caffeine-containing products, etc.) [30].
What is withdrawal syndrome ? WHO defines it as follows: it is a group of symptoms of varying clustering and severity that occur when the use of a psychoactive substance that has been used repeatedly, usually over a long period and/or in large doses, is stopped or reduced [31]. That is, in essence, this is a “breaking”, excuse the jargon. So, when a person does not consume caffeine for several hours (from 12 hours [22]), he begins to experience the following symptoms (Fig. 4):
- headache;
- fatigue;
- decreased energy;
- decreased attentiveness;
- drowsiness;
- irritability;
- problems with concentration;
- depressed mood;
and others [23].
Figure 3. Basic symbols for the following pictures
drawing by the author of the article
Figure 4. The mechanism of withdrawal syndrome formation in caffeine addiction. In the picture, 45 minutes and 2.5–4.5 hours correspond to the absorption time of caffeine into the blood and the half-life of caffeine, respectively. 12–24 hours reflects the average amount of time a person goes without consuming caffeine before experiencing withdrawal symptoms.
drawing by the author of the article
On the Internet, caffeine is often called a drug, but scientists have not reached a consensus on this issue. But we can say for sure that caffeine does not have the same impact on a person’s social life as drugs like opioids [32] or LSD [33].
How to safely quit caffeine
Try drinking plain water instead of cola first. Stick to this principle for a week. Have your caffeine cravings decreased? This means that the “treatment” must be continued. Now is the time to replace traditional coffee with a similar decaffeinated drink. It is also important to track portions of food consumption. Continue until your daily caffeine dose drops to 100 mg or less. Gradually giving up caffeine-containing drinks will protect you from unpleasant physiological sensations and will also be less “painful” on a psychological level.
Without caffeine, do you feel tired? Make sure you are getting enough rest per day? Better yet, check the vitamin and mineral balance in the body? Drowsiness and chronic fatigue may indicate vitamin deficiency or other health problems. But caffeine does not cure this.
What is it[edit]
Caffeine is a component of some common drinks that causes a surge of energy, gives energy, stimulates the brain, accelerates the pulse, and also enhances the effect of painkillers. This sounds great, but in small doses the stimulating effects are weak. Well, okay, you say, only after the end of the action the situation becomes completely opposite - even more fatigue sets in. If you smear yourself with caffeine in large quantities, then the chances of screwing up become much greater: the effect may actually be the opposite, after the end of the effect it becomes very bad, and if you consume more than a gram per day, addiction occurs. I’m talking about the physical one - you’ll get the psychological one much earlier.
In the human mind, caffeine is primarily associated with coffee (I wonder why?), in which it has a good concentration. It can also be found in tea, even in tea bags, as well as in soft drinks - Coca-Cola and its friends. In addition, caffeine is a component of energy drinks.
If you brew tea very actively and with a large amount of tea leaves, then there may be no less caffeine, or even more, than in the average mug of your instant Arabica coffee. Of course, you can increase the amount of the original product with both tea and coffee, but in the end you will simply ruin all the possible taste qualities of both drinks, lol.
Benefit for health
People who regularly consume caffeine (in adequate doses) report improved concentration and cognitive function. For some people it is a remedy for headaches.
According to some data, it can reduce the risk of Parkinson's disease, liver disease, dementia, and type 2 diabetes. But despite the possible positive effects, do not forget that consuming this substance in large doses can have adverse effects.
In addition, caffeine tablets serve as a cure for migraines. Take 1-2 tablets for a week, and then 1 tablet for a month. It also has benefits for bodybuilders, as it helps increase performance by almost 20%. Bodybuilders consume approximately 3 mg of the substance for every kilogram of body weight half an hour before a planned workout.
By the way, depression of the central nervous system, decreased activity (physical and mental), a state close to loss of consciousness, cerebral vascular spasms (migraine), hypotension and asthma can also be reasons to drink a cup of coffee or a tablet containing caffeine. Even infants are also prescribed this substance as a medicine for certain diseases.
Advantages:
- Reduces pain. Two cups of coffee can reduce post-workout pain by 48%.
- Source of fiber. Two cups of brewed coffee provides 1.8 g of fiber.
- Protection against diabetes. Coffee drinkers (1 cup per day) have a 9% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Immunity from Alzheimer's. There is an assumption that caffeine can protect against the development of Alzheimer's disease.
- Cure for depression. A 10-year study involving 86 thousand women showed that coffee drinkers were 20% less likely to suffer from depression.
- Protection against Parkinson's. Researchers from Sweden claim that caffeine reduces the chances of developing Parkinson's disease. Incredibly, scientists suggest that this substance can even affect the genetic factor.
- Protection against cardiac diseases. This generally sounds like science fiction, since traditional medicine prohibits people with heart problems from consuming caffeine. But Korean researchers say 3 cups of coffee a day improves health and reduces the chances of heart disease.
- Stronger DNA. The European Journal of Nutrition once reported that the DNA of coffee drinkers is more stable and without damage. They say that this is again due to caffeine.
- Less chance of multiple sclerosis – 4 cups of caffeinated beverage per day can protect against multiple sclerosis, preventing neuronal damage that causes the disease. At least that's what researchers from Sweden think.
- Reduces the risk of cancer. Moderate caffeine consumption reduces the risk of colon cancer by 26%. This was stated by scientists from California after a study involving 5,100 people. And another group of scientists from a cancer center in Southern California noticed that coffee drinkers were 29% less likely to get liver cancer.
- No gout. A study involving more than 50 thousand people allowed scientists to conclude that coffee protects men from gout. It is believed that this is the “work” of caffeine. Although no one can give a 100% guarantee of this yet. Moreover, there is a completely opposite opinion that it is precisely this that causes gout.
In addition, some experiments have shown that caffeine can stimulate sexual desire in women, protect against early death (according to Japanese scientists), prevent tooth decay, retinal damage and even melanoma.
Where does adenosine come from in the brain?
There are several sources:
- ATP hydrolysis [7].
- The result of the activity of glial cells [1].
- Others [7].
But the main supplier is ATP. The human brain consumes up to 25% of the body’s total energy [8]. He gets it mainly from adenosine triphosphate. From the abbreviation you can understand the structure of the molecule: adenosine and three phosphate molecules. Energy is released through the hydrolysis of ATP. In one of his lectures at Postnauka, Vyacheslav Dubynin gave a good analogy with this process [9]. He compared ATP hydrolysis to shooting from a pistol. There are only three shots (three opportunities to split off the phosphate molecules), and each shot releases energy that the body's cells use for various processes. And after three shots, as you might guess, only an adenosine molecule remains. During the day, adenosine accumulates, both intracellularly and extracellularly. Intracellular adenosine leaves the cell using special transport systems.
Next, adenosine begins to interact with adenosine receptors (Fig. 1) [7], [10]. There are four types of receptors in total: A1, A2A, A2B, A3. They are located on neurons, as well as on cells of other organs (heart, kidneys, etc.). All four types are combined into the superfamily of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) [7], about which there are many interesting articles on Biomolecule. You can read more about the 3D structure of adenosine receptors in the article “Structures of GPCR receptors in the piggy bank” [11]. Each of these receptors has its own ligands (substances that bind to the receptor) - agonists and antagonists. “So, what else is this?” - you ask. Nothing complicated really. Agonists are substances that can bind to a receptor and lead to a specific effect (positive or negative). Antagonists can only bind to the receptor, but this will not lead to any effect. So, essentially, they block the receptor from binding to the agonist. What are the agonists and antagonists for adenosine receptors? In fact, there are many substances (if you are interested, you can read about it in [4]), but I will consider two of them: adenosine and caffeine. The former is an agonist and the latter an antagonist of adenosine receptors [7], [10].
Another article about adenosine receptors is participating in the competition: “Adenosine receptors: the story of the great deception” [12]. - Ed.
Figure 1. Structure of adenosine and its mechanism of action. The chemical formula of adenosine is presented, where oxygen molecules are indicated in red and nitrogen molecules in blue. As depicted in the figure, the receptor consists of exactly seven domains—a distinctive feature of all four types of adenosine receptors. The pink flow reflects the effect of adenosine on the cell.
drawing by the author of the article
So, what effect does adenosine have when it binds to receptors? The role of adenosine in sleep induction has been well studied [1], [13–16]. Essentially, it makes us sleepy, albeit with some caveats, and this is a very interesting mechanism. Brain cells work for a long time, a lot of adenosine accumulates, it binds to adenosine receptors, and the cells receive a signal that it is time to “rest.” These processes allow neurons not to overstrain.
However, if you go deeper, everything is more complicated. Not all mechanisms are still understood. By interacting with different receptors, adenosine leads to different effects. Moreover, there is evidence that by interacting with the same receptor (for example, with A1A) in one region of the brain, adenosine can induce sleep, and by binding in another - awakening [1].
What does a caffeine molecule look like?
Let's take a closer look at the structure of the caffeine molecule. This will help you understand how it works. Scientists have found that raw coffee beans contain half the carbohydrates. They are a kind of fuel for our body. They give energy to every cell of ours. These carbohydrates are mainly simple sugars (fructose, sucrose) and polysaccharides (fiber, cellulose, pectin). These substances are simply irreplaceable for our brain. They are directly involved in its nutrition. Sugars and polysaccharides nourish nerve cells. This ensures normal functioning of the brain and nervous system.
Coffee also contains minerals:
- magnesium;
- potassium;
- calcium.
These are the most important minerals of inorganic origin. They are found in bones and muscles. Without them, proper functioning of blood vessels and the brain is impossible. These minerals ensure the normal functioning of the heart muscle. Scientists have found that raw coffee beans contain about 850 different essential compounds. But in the fried product their quantity is reduced by almost two and a half times and amounts to 350 units. They provide the amazing aroma of coffee. It is not surprising that this drink has long been recognized as the most fragrant.
What nutritional value does coffee have?
Like any product, coffee has its own nutritional value. As you know, it is measured in calories. Let’s immediately make a reservation that natural black coffee without sugar and other additives has a minimum amount of calories. This is explained by the fact that the substances it contains are very easily absorbed. The body easily absorbs them and quickly digests them. This process is also stimulated by caffeine, which is found in large quantities in coffee beans. So everyone. Anyone who doesn’t want to gain extra pounds can be recommended to regularly drink a cup of natural, fresh coffee. But to avoid complications, you should drink no more than two cups of this weak drink per day. To prevent your body from being overloaded with calories, it is better not to add sugar, cream or milk to your coffee. The ideal option is black coffee without sugar. If you have a sweet tooth and don’t like to feel the bitter taste in your mouth from coffee, then add a little sugar to it. One teaspoon will be enough.
How healthy is coffee?
If you regularly drink this invigorating drink, you must be wondering how beneficial it is for our body. The type of coffee and method of preparation also play an important role. This product is rich in proteins, fats, it contains vitamins A, B, E, D, as well as such important minerals as phosphorus, potassium, calcium. All these substances provide the effect that coffee has on the body. It can be either positive or negative. This contradictory influence is due to the fact that coffee contains simply a huge number of components. Each of them affects our body in its own way. In addition, a person may have individual susceptibility to them. It is also important how much drink a person drinks per day, what concentration.
Doctors have calculated a safe dose of coffee for humans - a couple of cups per day. However, you should not brew a drink that is too strong. Try to brew coffee of medium concentration, and do not drink it more than twice a day. Also, do not drink coffee later than 4 hours before bedtime.
Let's take a closer look at exactly how coffee affects our body. Here are the main characteristics of its effect on the human body:
- If you regularly drink strong enough coffee, you can cause coffee addiction. To do this, you need to drink an amount of coffee per day that contains about 1000 mg of caffeine. This is what causes the addictive phenomenon. This addiction is very similar to alcohol or nicotine addiction. Getting used to coffee is that over time, the substances begin to have less and less pronounced effects on a person who drinks this drink in sufficiently large quantities. If at first coffee invigorates well and stimulates performance, then as you get used to it, this effect becomes less pronounced. To get the initial effect, a person is forced to drink more and more coffee. This is where getting used to it begins.
- Diuretic effect. Scientists have long noticed. That coffee has a pronounced diuretic effect. True, it doesn't last long. At the same time, excess fluid is removed from the body. This is why it is recommended to drink coffee for swelling. But if you eat or drink too much of it, you risk getting dehydrated. And this is already fraught with disruption of the functioning of internal organs. To prevent disastrous consequences, nutritionists recommend not overusing coffee. After you've enjoyed a cup of coffee, drink a glass of clean water and you won't get dehydrated. If you still brought it to this. When the first signs of dehydration begin to appear, just start drinking more. For this, clean, unboiled water, preferably bottled, is best suited. You can also supplement it with a glass of mineral water. It will replenish mineral deficiency.
- Coffee may slightly increase your blood pressure. This effect is due to the fact that this invigorating drink stimulates blood vessels. They become toned, and the pressure rises slightly. That is why it is not recommended to drink coffee for those who suffer from hypertension. This drink can immediately increase blood pressure by 15 mmHg. Moreover, this indicator applies to those coffee lovers who do not suffer from various vascular and heart diseases. But for the latter, pressure readings can jump significantly higher than 15 mm. But for some people, after drinking coffee, their blood pressure may, on the contrary, drop. This reaction of the body is due to the fact that coffee has a diuretic effect. This may also be due to the individual characteristics of the body. But basically, coffee is very useful for those who are prone to low blood pressure. In hypotensive patients, after a cup of aromatic drink, blood pressure can stabilize, performance increases, and headaches go away.
- Coffee may affect the functioning of the heart. True, this influence is indirect. But indirectly this drink affects the functioning of the heart in the following way. After that. As caffeine enters the body, the nervous system is stimulated. After stimulation of the central nervous system, blood pressure increases. But the increased pressure itself begins to stimulate the heart. It accelerates its rhythm, the load on it increases. The degree of increase in load will depend on the dose of caffeine, the general condition of the body, as well as the individual sensitivity of the coffee components.
- Drinking unfiltered coffee regularly can cause an increase in cholesterol levels in your blood. This is extremely undesirable, since elevated cholesterol levels lead to blockage of blood vessels and their pathologies. This is fraught with problems with blood pressure. Over time, a stroke or heart attack may even develop.
- Coffee can increase the level of attention and stimulate memory. This effect is associated with its effect on the central nervous system. After stimulating the nervous system, a person’s brain activity improves. This means that coffee can actually improve performance. But this phenomenon is temporary. The pronounced effect does not last long - from half an hour to two hours after drinking the coffee. Interestingly, this drink can also improve your mood. It is even recommended to drink it in the initial stages of depression. The effect of the drink on the body will also depend on the individual characteristics of the person and his state of health.
- The effect of some medications may be enhanced. We are talking, first of all, about the effect of painkillers. Caffeine enhances the effect of analgin and acetylsalicylic acid.
- Interestingly, according to scientists, caffeine reduces the risk of developing Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. This is due to the fact that it directly affects the neurons of our brain, and also temporarily constricts blood vessels. At the same time, the brain and blood vessels receive a kind of training.
- If you regularly drink natural coffee, you will begin to suffer less from constipation.
- The risk of developing liver pathologies, in particular cirrhosis, is reduced.
- Women are less likely to develop breast cancer.
- In older people, coffee can reduce bone density. This is due to its diuretic effect. Since in old age calcium is absorbed worse, and with a diuretic effect it is washed out faster. This can lead to brittle bones. This increases the risk of cracks and fractures.
- Urolithiasis may develop. This applies, first of all, to those coffee lovers who drink more than two cups a day.
- It is not recommended to drink coffee during pregnancy and lactation. It can cause increased blood pressure and negatively affect the fetus. Anemia of the placenta and even miscarriage may also develop. Coffee can cause low weight gain in newborns.
So, we tried to tell you as clearly as possible about the composition of coffee beans. Now you know its main components and their effect on the human body.
Recommended:
- How coffee affects the body
- Coffee and cholesterol
- Can people with high cholesterol drink coffee?
- Coffee and the digestive tract
- How many calories are in coffee
- How instant coffee is made